Lower back pain is a common issue that affects millions of people worldwide, often disrupting daily activities and reducing quality of life. Whether it’s caused by poor posture, heavy lifting, or underlying health conditions, the discomfort can be both persistent and debilitating. Given its prevalence, finding effective and quick remedies to manage lower back pain is essential for maintaining an active and healthy lifestyle.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Quick remedies are crucial because they provide immediate relief, allowing individuals to continue with their daily routines without being sidelined by lower back pain. They also offer practical solutions that can be easily incorporated into anyone’s schedule, whether at home or on the go.
In this article, we will explore seven quick remedies that can help alleviate lower back pain. These remedies include simple stretching exercises, over-the-counter lower back pain relievers, heat and cold therapy, gentle physical activity, proper posture techniques, and massage therapy. By implementing these strategies, you can find fast relief and improve your overall back health.
Lower Back Pain: 7 Quick Remedies
1. Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises are a highly effective way to alleviate lower back pain. They work by improving flexibility, increasing blood flow to the muscles, and reducing tension in the back. Regular stretching can help prevent future pain by strengthening the muscles that support the spine and improving overall posture. Importance of stretching and specific exercises Harvard Health Publishing: Stretching.
Explanation of How Stretching Can Alleviate Lower Back Pain
Stretching helps to elongate the muscles and soft tissues around the spine, which can relieve tightness and reduce the strain on the lower back. By increasing the range of motion in the hips, pelvis, and lower spine, stretching exercises can help distribute the stress more evenly across the body’s structures, thereby reducing the lower back pain.
Description of Specific Stretches
1. Child’s Pose
- How to Do It: Start on your hands and knees. Sit back on your heels and extend your arms forward, lowering your chest towards the ground. Hold this position for 20-30 seconds, breathing deeply.
- Benefits: This stretch gently elongates the spine and relieves tension in the lower back.
2. Cat-Cow Stretch
- How to Do It: Begin on your hands and knees. Inhale as you arch your back (cow position), lifting your head and tailbone. Exhale as you round your back (cat position), tucking your chin and tailbone. Repeat this sequence for 10-15 repetitions.
- Benefits: This dynamic stretch improves flexibility and mobility in the spine, reducing stiffness and lower back pain.
3. Knee-to-Chest Stretch
- How to Do It: Lie on your back with your knees bent. Bring one knee up to your chest, holding it with both hands. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then switch to the other leg. Repeat 2-3 times for each leg.
- Benefits: This stretch targets the lower back and hips, relieving tension and improving flexibility.
Tips on How to Perform These Stretches Safely
- Warm-Up: Always warm up your body with light activities, such as walking or marching in place, before stretching to avoid muscle strain.
- Listen to Your Body: Stretch to the point of mild discomfort, not lower back pain. If a stretch feels too intense, ease off slightly.
- Breathe Deeply: Maintain steady and deep breathing during each stretch to help relax the muscles.
- Maintain Proper Form: Ensure your body is aligned correctly during each stretch to prevent injury. Use a mirror or seek guidance if you’re unsure about your form.
- Gradual Progression: Increase the duration and intensity of your stretches gradually over time to improve flexibility without risking injury.
Incorporating these stretching exercises into your daily routine can provide significant relief from lower back pain and improve your overall back health.
2. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers are a convenient and effective option for managing lower back pain. These medications can help reduce inflammation, alleviate lower back pain, and improve your ability to perform daily activities. Two of the most commonly used OTC pain relievers are ibuprofen and acetaminophen.
Discussion on the Effectiveness of OTC Medications
Ibuprofen:
- Effectiveness: Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that works by reducing inflammation and lower back pain. It is particularly effective for conditions where inflammation is a primary cause of lower back pain, such as muscle strains or arthritis.
- Common Brands: Advil, Motrin
Acetaminophen:
- Effectiveness: Acetaminophen works by blocking pain signals in the brain. It is effective for relieving mild to moderate lower back pain and is a good option for individuals who cannot take NSAIDs.
- Common Brands: Tylenol
Both medications can be effective for short-term relief of lower back pain, helping you manage discomfort and maintain your daily routine.
Recommended Dosages and Potential Side Effects
Ibuprofen:
- Dosage: The typical adult dose is 200-400 mg every 4-6 hours as needed, not exceeding 3200 mg per day.
- Potential Side Effects: Common side effects include stomach upset, heartburn, and dizziness. Long-term use or high doses can increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, kidney damage, and cardiovascular issues.
Acetaminophen:
- Dosage: The typical adult dose is 500-1000 mg every 4-6 hours as needed, not exceeding 3000 mg per day (or 4000 mg if advised by a healthcare provider).
- Potential Side Effects: Acetaminophen is generally well-tolerated, but overuse can lead to liver damage, especially if combined with alcohol consumption.
Importance of Consulting with a Healthcare Provider Before Use
While OTC pain relievers are readily available and generally safe when used as directed, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any medication regimen. This is especially important if you have pre-existing health conditions, are taking other medications, or are unsure about the appropriate dosage. A healthcare provider can help you choose the most suitable medication and dosage, and provide guidance on how to minimize potential side effects and risks.
Using OTC pain relievers responsibly can be an effective part of your strategy to manage lower back pain, providing relief and allowing you to stay active and engaged in your daily life.
3. Heat Therapy
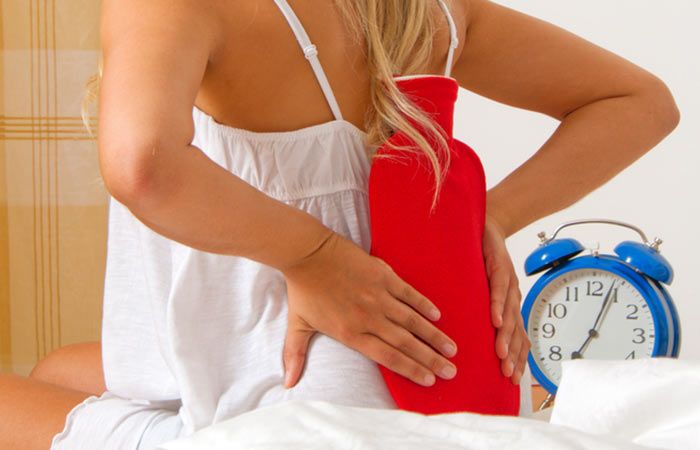

Heat therapy is a simple yet powerful method for relieving lower back pain. Applying heat to the affected area can provide immediate comfort and facilitate the healing process by improving blood flow and relaxing tense muscles.
Benefits of Using Heat Packs or Warm Baths
Heat Packs:
- Heat packs, whether electric or microwaveable, offer a convenient way to target specific areas of discomfort. They are portable, easy to use, and can provide sustained heat over a period of time.
- Warm Baths:
Warm baths can envelop the entire lower back in soothing heat, providing comprehensive relief. Adding Epsom salts to the bath can enhance the therapeutic effects by reducing muscle soreness and inflammation.
How Heat Helps to Relax Muscles and Reduce Pain
Muscle Relaxation:
Heat increases the temperature of the tissues in the affected area, which helps to relax muscles and alleviate spasms. This relaxation reduces stiffness and improves the flexibility of muscles and connective tissues, making movement easier and less painful.
Increased Blood Flow:
Applying heat stimulates blood flow to the area, which can help deliver oxygen and nutrients to the damaged tissues, promoting healing. Improved circulation also helps to remove waste products from the muscles, reducing inflammation and discomfort.
Pain Relief:
Heat can help to reduce pain signals sent to the brain, effectively decreasing the perception of lower back pain. This soothing effect can provide significant relief, making it easier to engage in daily activities.
Guidelines for Using Heat Therapy Effectively
Types of Heat Therapy:
- Moist Heat: Moist heat, such as warm baths or damp heat packs, penetrates deeper into the muscles and provides more effective relief than dry heat.
- Dry Heat: Dry heat, such as electric heating pads or hot water bottles, can also be effective and is more convenient for long-term use.
Duration and Frequency:
- Apply heat for 15-20 minutes at a time, allowing enough time for the heat to penetrate the muscles without causing burns or overheating.
- Use heat therapy 2-3 times a day, depending on the severity of the lower back pain and your personal comfort.
Safety Tips:
- Avoid Prolonged Use: Do not use heat therapy for extended periods as it can cause skin burns and irritation. Always follow the recommended duration.
- Temperature Control: Ensure that the heat pack or bath is at a comfortable, warm temperature. It should be hot enough to be effective but not so hot that it causes discomfort or burns.
- Protect Your Skin: Place a cloth or towel between your skin and the heat source to prevent direct contact and reduce the risk of burns.
- Monitor Your Skin: Check your skin periodically during heat therapy to ensure there is no redness or irritation.
By following these guidelines, you can use heat therapy effectively to relax muscles, increase blood flow, and reduce lower back pain, providing much-needed relief from lower back discomfort.
4. Cold Therapy
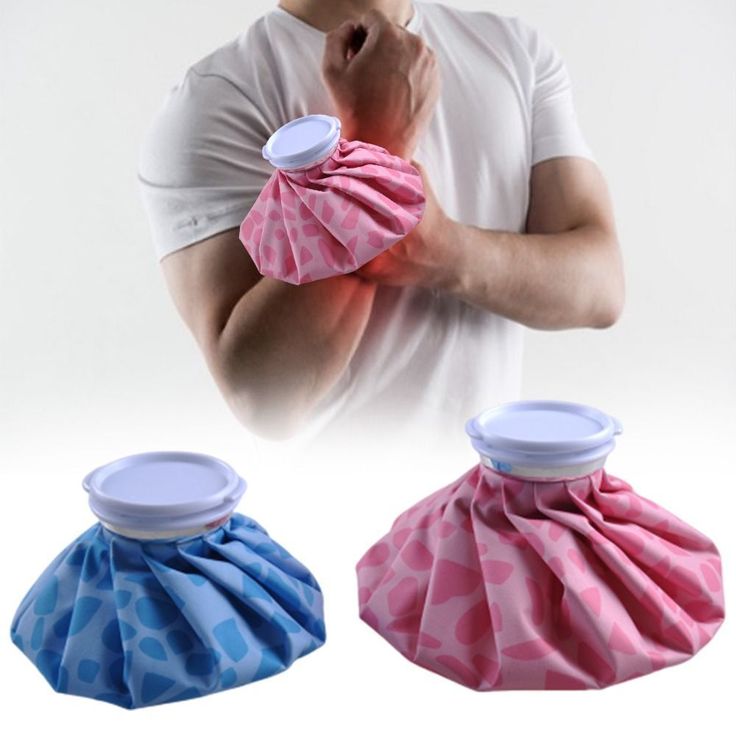

Cold therapy, also known as cryotherapy, is an effective method for reducing lower back pain, especially in the initial stages of injury or when inflammation is present. Applying cold packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation, numb pain, and limit swelling.
Explanation of How Cold Packs Can Reduce Inflammation and Numb the Pain
Reduce Inflammation:
Cold therapy constricts blood vessels in the area where it is applied, which helps to reduce blood flow and limit inflammation and swelling. This is particularly useful in the first 48 hours after an injury or when there is noticeable swelling.
Numb the Pain:
Cold packs provide a numbing effect on the lower back pain receptors, temporarily decreasing the sensation of pain. This can offer immediate relief and make it easier to manage discomfort during activities.
Instructions on Proper Application of Cold Therapy
Type of Cold Packs:
- Commercial Cold Packs: These are readily available and designed for easy application.
- Homemade Cold Packs: A bag of frozen vegetables or a mixture of water and rubbing alcohol in a plastic bag can serve as an effective cold pack.
Application Steps:
- Prepare the Cold Pack: Ensure the cold pack is at an appropriate temperature. It should be cold but not frozen solid to prevent frostbite.
- Protect Your Skin: Always wrap the cold pack in a thin cloth or towel to avoid direct contact with the skin, which can cause ice burns.
- Apply to Affected Area: Place the cold pack on the painful area of your lower back.
- Duration: Keep the cold pack on the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time.
- Frequency: Use cold therapy every 2-3 hours during the first 48 hours after the onset of lower back pain or injury.
Safety Tips:
- Monitor the Skin: Check your skin periodically to ensure there is no excessive redness or frostbite.
- Limit Exposure: Do not apply cold packs for longer than recommended as prolonged exposure can damage skin and underlying tissues.
Tips on Alternating Between Heat and Cold Therapies
When to Use Cold Therapy:
- Use cold therapy during the acute phase of injury (first 48 hours) to reduce inflammation and numb pain.
- Apply cold packs immediately after activities that might aggravate the lower back pain.
When to Use Heat Therapy:
- Use heat therapy after the initial acute phase (post 48 hours) to relax muscles, increase blood flow, and promote healing.
- Apply heat before activities to warm up muscles and prevent stiffness.
Alternating Tips:
- Transition Gradually: When alternating between cold and heat, allow your skin to return to normal temperature before switching.
- Combined Approach: For chronic lower back pain, some people find relief using heat in the morning to loosen muscles and cold in the evening to reduce inflammation after a day’s activity.
- Personal Preference: Experiment with the duration and frequency of both therapies to find what works best for your lower back pain relief and comfort.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively use cold therapy to manage lower back pain, reduce inflammation, and provide immediate lower back pain relief. Alternating between cold and heat therapies can offer a balanced approach to lower back pain management and recovery.
5. Gentle Physical Activity
Engaging in gentle physical activity is crucial for managing and preventing lower back pain. Staying active helps maintain flexibility, strength, and overall health, while prolonged bed rest can lead to stiffness and increased lower back pain.
Importance of Staying Active and Avoiding Prolonged Bed Rest
Staying Active:
Maintaining regular physical activity ensures that the muscles and joints stay flexible and strong. Movement helps to keep the blood flowing, which can reduce stiffness and pain in the lower back. It also promotes the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, which can help to alleviate discomfort and improve mood.
Avoiding Prolonged Bed Rest:
While it might seem intuitive to rest completely when experiencing lower back pain, prolonged bed rest can actually worsen the condition. Extended periods of inactivity can lead to muscle atrophy (weakening), joint stiffness, and a reduction in overall physical fitness, making it harder to recover and more likely to experience future episodes of pain.
Examples of Gentle Activities
Walking:
- Walking is a low-impact exercise that can be easily incorporated into daily routines. It helps to increase circulation, strengthen muscles, and improve flexibility without putting excessive strain on the back.
- Tips: Start with short walks and gradually increase the duration. Wear comfortable shoes and maintain good posture to maximize benefits.
Swimming:
- Swimming and water aerobics provide an excellent workout for the entire body while minimizing stress on the joints. The buoyancy of water supports the body, reducing the impact on the lower back and allowing for a greater range of motion.
- Tips: Focus on gentle strokes and avoid movements that twist or strain the back. Swimming with a float or doing water walking can also be beneficial.
Yoga and Stretching:
- Gentle yoga and stretching exercises can help improve flexibility, strength, and balance. Specific poses and stretches can target the lower back, helping to relieve tension and lower back pain.
- Tips: Choose beginner-friendly yoga routines and avoid poses that cause discomfort. Consider using props like blocks or straps for support.
Pilates:
- Pilates focuses on strengthening the core muscles, which support the spine and can help alleviate lower back pain. Gentle Pilates exercises can improve posture, flexibility, and overall body awareness.
- Tips: Start with basic exercises and gradually progress as your strength improves. It’s important to maintain proper form to avoid injury.
Benefits of Physical Activity for Long-Term Back Health
Improved Flexibility and Mobility:
Regular physical activity helps to maintain and improve flexibility and mobility in the muscles and joints. This can reduce the risk of stiffness and make everyday movements easier and less painful.
Stronger Muscles:
Strengthening the muscles, particularly those in the core and lower back, provides better support for the spine. Strong muscles can absorb more stress and reduce the likelihood of injury and lower back pain.
Enhanced Posture:
Physical activity, especially exercises that focus on core strength and alignment, can improve posture. Good posture reduces the strain on the lower back and helps to prevent lower back pain associated with poor alignment.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight through physical activity reduces the stress placed on the lower back. Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can shift the body’s center of gravity and increase the risk of lower back pain.
Reduced Risk of Recurrence:
Staying active helps to keep the back muscles and joints in good condition, reducing the likelihood of recurring lower back pain. Regular exercise also promotes overall health and well-being, contributing to a lower risk of developing chronic pain conditions.
Incorporating gentle physical activity into your daily routine is a key component of managing and preventing lower back pain. These activities not only provide immediate relief but also contribute to long-term back health and overall well-being.
6. Proper Posture
Maintaining proper posture is essential for preventing and alleviating lower back pain. Poor posture can place undue stress on the spine and surrounding muscles, leading to discomfort and long-term issues. By adopting good posture habits, you can reduce the strain on your lower back and promote overall spine health.
How Poor Posture Can Exacerbate Lower Back Pain
Increased Strain on the Spine:
When you slouch or sit with a rounded back, the natural curve of the spine is disrupted. This can lead to increased pressure on the intervertebral discs and spinal joints, causing lower back pain and discomfort.
Muscle Imbalance and Fatigue:
Poor posture can cause certain muscles to become overworked while others weaken. For example, slumping forward can overextend the muscles in the lower back and hip flexors, leading to muscle fatigue and imbalance, which exacerbates pain.
Reduced Circulation:
Sitting or standing with poor posture can impede blood flow, which is essential for delivering nutrients and oxygen to the muscles and tissues. Reduced circulation can contribute to muscle stiffness and pain.
Tips for Maintaining Good Posture Throughout the Day
Standing Posture:
- Align Your Ears, Shoulders, and Hips: Stand with your ears aligned over your shoulders and your shoulders aligned over your hips. This helps maintain the spine’s natural curve.
- Engage Your Core: Lightly engage your abdominal muscles to support your lower back.
- Distribute Weight Evenly: Stand with your feet hip-width apart and distribute your weight evenly between both feet. Avoid locking your knees.
Sitting Posture:
- Sit Back in Your Chair: Ensure your lower back is fully supported by the chair’s backrest. Use a small cushion or lumbar roll if needed.
- Feet Flat on the Floor: Keep your feet flat on the floor or on a footrest, with your knees at a 90-degree angle.
- Shoulders Relaxed: Keep your shoulders relaxed and avoid hunching forward. Your screen should be at eye level to prevent neck strain.
Sleeping Posture:
- Use a Supportive Mattress: A medium-firm mattress can provide adequate support for your spine.
- Side Sleeping: If you sleep on your side, place a pillow between your knees to maintain proper spinal alignment.
- Back Sleeping: If you sleep on your back, place a pillow under your knees to reduce pressure on your lower back.
Ergonomic Adjustments for Work and Home Environments
Workspace Setup:
- Desk Height: Ensure your desk is at a height where your forearms are parallel to the floor when typing.
- Chair Support: Use an ergonomic chair that supports the natural curve of your spine. Adjust the chair height so your feet are flat on the floor.
- Monitor Position: Place your monitor at eye level to avoid tilting your head forward. The top of the screen should be at or just below eye level.
Keyboard and Mouse:
- Keyboard Position: Keep your keyboard close enough so you can type with your elbows at your sides, forming a 90-degree angle.
- Mouse Placement: Position your mouse next to the keyboard and use a mouse pad with wrist support to maintain a neutral wrist position.
Frequent Breaks:
- Move Regularly: Avoid sitting or standing in one position for too long. Take breaks to walk around and stretch every 30 minutes.
- Stretching: Incorporate stretches that target the neck, shoulders, and lower back into your daily routine to maintain flexibility and reduce tension.
By following these tips and making ergonomic adjustments in your work and home environments, you can maintain good posture, reduce the strain on your lower back, and prevent lower back pain. Good posture is a crucial aspect of long-term back health and overall well-being.
7. Massage Therapy
Massage therapy is a highly effective method for relieving lower back pain. It works by relaxing muscle tension, improving circulation, and promoting the release of endorphins, which are the body’s natural painkillers. Whether done by a professional or through self-massage techniques, regular massage can significantly improve your back health and overall well-being.
Overview of How Massage Can Relieve Muscle Tension and Improve Circulation
Relieve Muscle Tension:
Massage therapy targets the muscles and soft tissues, helping to release tight knots and areas of tension. By applying pressure and using various techniques, massage can relax stiff muscles, reduce spasms, and improve flexibility.
Improve Circulation:
Massage increases blood flow to the affected areas, delivering oxygen and nutrients necessary for healing. Improved circulation also helps to remove metabolic waste products from the muscles, reducing inflammation and promoting quicker recovery.
Endorphin Release:
Massage stimulates the release of endorphins, which are chemicals in the brain that act as natural pain relievers. This can help reduce the perception of lower back pain and create a sense of well-being and relaxation.
Types of Massages That Are Particularly Effective for Lower Back Pain
Swedish Massage:
- Description: This is a gentle form of massage that uses long strokes, kneading, deep circular movements, vibration, and tapping.
- Benefits: Swedish massage can help relax the entire body, improve circulation, and relieve muscle tension, making it beneficial for general lower back pain relief.
Deep Tissue Massage:
- Description: This massage technique focuses on the deeper layers of muscle and connective tissue. It involves slower, more forceful strokes to target deep-seated muscle tension and knots.
- Benefits: Deep tissue massage is particularly effective for chronic lower back pain caused by muscle adhesions or overuse injuries.
Trigger Point Massage:
- Description: This technique involves applying pressure to specific points in the muscles that are causing lower back pain or referred pain in other areas.
- Benefits: Trigger point massage can help relieve pain and tension in the lower back by targeting and releasing these specific points.
Hot Stone Massage:
- Description: Heated stones are placed on specific parts of the body and used as tools by the therapist to massage the muscles.
- Benefits: The heat from the stones helps to relax muscles and improve blood flow, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the massage.
Advice on Seeking Professional Help or Using Self-Massage Techniques
Seeking Professional Help:
- Licensed Therapist: Look for a licensed massage therapist with experience in treating lower back pain. They can provide tailored treatments based on your specific needs.
- Regular Sessions: Consistent massage therapy sessions can provide cumulative benefits, helping to manage and prevent lower back pain over time.
- Communication: Clearly communicate your pain points and any discomfort you experience during the massage to ensure the therapist can adjust their techniques accordingly.
Using Self-Massage Techniques:
- Foam Roller: Use a foam roller to apply pressure to your lower back muscles. Roll slowly over the affected areas, pausing on any tight spots to help release tension.
- Tennis Ball: Place a tennis ball between your lower back and the wall or floor. Gently roll the ball over the muscles, focusing on areas of tightness or discomfort.
- Massage Tools: Handheld massagers or electric massage devices can be used to target specific areas of the lower back. Ensure you use these tools according to the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid injury.
- Self-Massage Techniques: Use your hands to apply gentle pressure and kneading motions to your lower back. Start with light pressure and gradually increase as your muscles begin to relax.
Incorporating massage therapy into your routine can provide significant relief from lower back pain, improve circulation, and promote overall muscle relaxation. Whether you choose professional massage services or self-massage techniques, regular massage can be an invaluable part of your pain management and wellness strategy.
Lower back pain is a common and often debilitating issue, but there are effective remedies that can provide quick relief and improve overall back health. Let’s recap the seven quick remedies discussed:
- Stretching Exercises: Incorporate stretches like the child’s pose and cat-cow stretch to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Use medications like ibuprofen and acetaminophen to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation, following recommended dosages.
- Heat Therapy: Apply heat packs or take warm baths to relax muscles and enhance blood flow, promoting healing.
- Cold Therapy: Use cold packs to reduce inflammation and numb pain, particularly effective within the first 48 hours of pain onset.
- Gentle Physical Activity: Engage in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or yoga to maintain flexibility and strength.
- Proper Posture: Maintain good posture throughout the day and make ergonomic adjustments in your environment to reduce strain on your lower back.
- Massage Therapy: Seek professional massage therapy or use self-massage techniques to relieve muscle tension and improve circulation.
Encouragement
If you experience persistent or severe lower back pain, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your needs. Trying these remedies can offer significant relief and help manage lower back pain effectively.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining a healthy back is essential for overall well-being and quality of life. Regularly practicing these quick remedies can prevent future pain and promote long-term back health. Staying active, paying attention to posture, and seeking appropriate medical advice when necessary are key steps to ensure your back remains strong and pain-free. By taking proactive measures and incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can enjoy a more comfortable and active lifestyle.